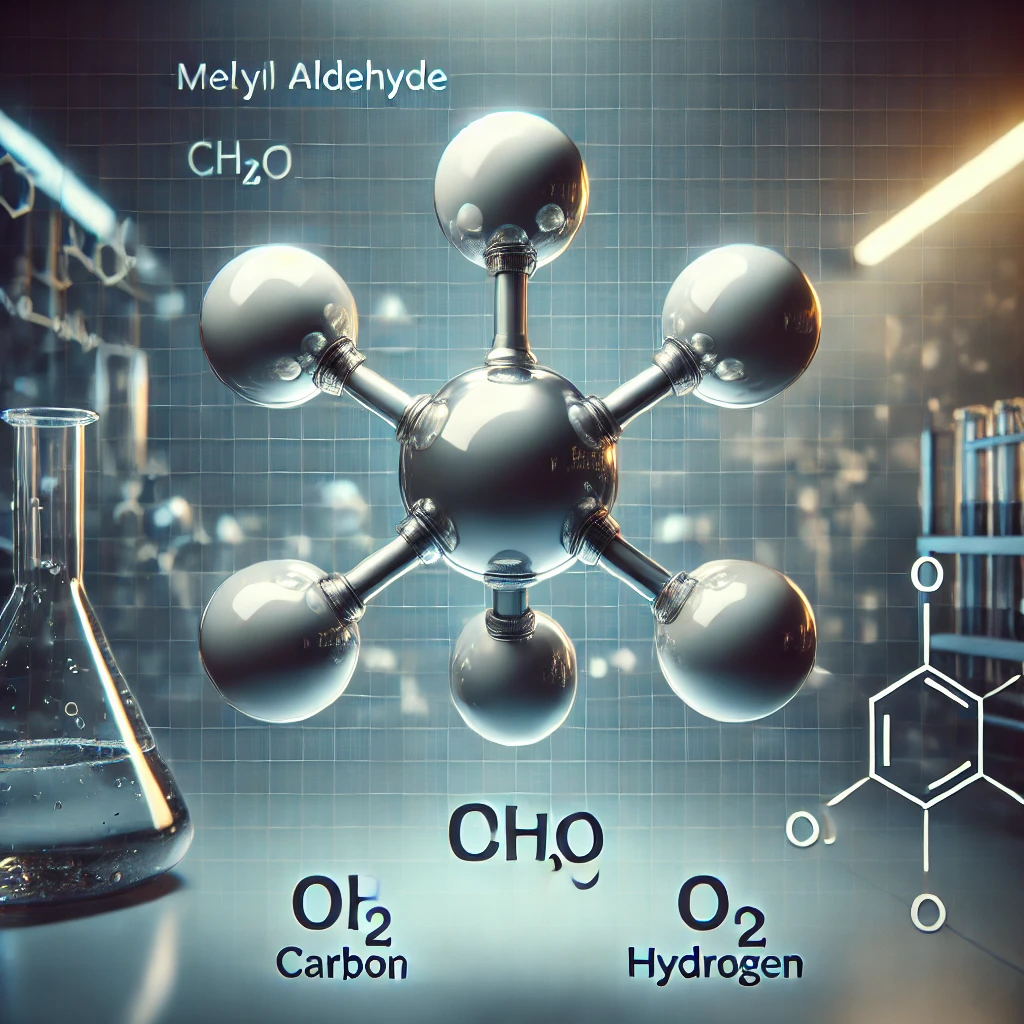
CH2O-Methyl Aldehyde
Methyl aldehyde (CH₂O), commonly known as formaldehyde, is a reactive aldehyde used in resin production, disinfection, textile treatment, and chemical synthesis.
Methyl Aldehyde (CH₂O) – Properties, Applications, and Safety Information
Also Known As: Formaldehyde
Chemical Name: Methyl Aldehyde
Chemical Formula: CH₂O
Chemical Class: Aldehydes, Organic Compounds
Physical and Chemical Properties
-
Molecular Weight: 30.03 g/mol
-
Boiling Point: –19.5 °C
-
Melting Point: –92.0 °C
-
Density: 0.815 g/cm³ (37% aqueous solution)
-
Solubility: Fully soluble in water; also miscible with alcohol and ether
-
Reactivity: Reacts with oxidizing and reducing agents; may polymerize upon exposure to light or heat
-
Stability: Stable at room temperature but volatile and flammable
Applications
✅ Resin production – Key intermediate in urea-formaldehyde and phenol-formaldehyde resin manufacturing
✅ Textile and paper finishing – Used as a binding and stiffening agent
✅ Disinfection and preservation – Applied in healthcare and labs as a disinfectant and tissue fixative
✅ Agricultural chemicals – Used in the production of pesticides and fertilizers
✅ Chemical synthesis – Serves as a base chemical for many organic compounds
Safety Information
⚠️ Carcinogenic – Prolonged exposure may increase cancer risk
❗ Irritating – Causes eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation
❗ Volatile and flammable – Requires controlled storage and handling
✅ Storage – Keep in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and heat sources
✅ PPE: Chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, solvent respirator, lab coat